Quick Answer: Antifreeze keeps your engine’s cooling system in top shape by lowering the freezing point and raising the boiling point of the coolant, protecting it against temperature extremes. It also helps transfer heat, prevents corrosion, and ensures your engine runs smoothly year-round.
Chilling Truths: How Antifreeze Keeps Engines Alive
Imagine your engine as a hardworking athlete—it generates a lot of heat when running, but can also be exposed to freezing cold in winter. Without some clever chemistry, both extremes could damage it. Antifreeze, mixed with water to form coolant, makes sure the liquid in your engine cooling system doesn’t freeze on frigid days or boil away in summer heat. This expanded temperature range maintains steady engine temperature regulation, prevents engine block cracking from ice, and protects against overheating damage.
Pure water freezes at 32°F (0°C) and boils at 212°F (100°C), but a common 50/50 water–ethylene glycol mix can freeze only around -35°F (-37°C) and boil closer to 223°F (106°C). That’s a big protective umbrella for your vehicle’s health.
Colligative Properties in Action
The starring scientific principle here is called colligative properties. These don’t depend on which chemical you’re using, but on how many particles are dissolved in the water. When glycol molecules mix with water, they mess with ice crystal formation, pushing the freezing point down—a process called freezing point depression. They also slightly lower the coolant’s vapor pressure, raising its boiling point and helping avoid vaporization at normal operating temperatures.
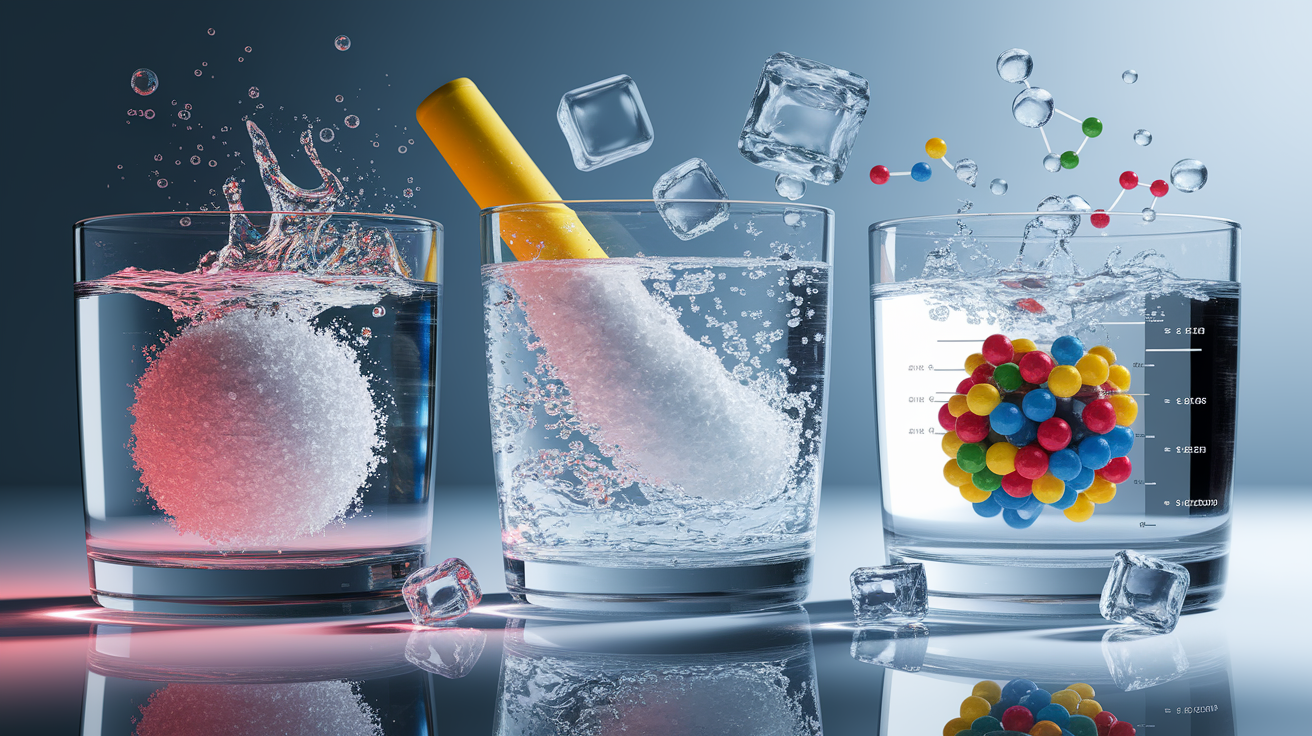

- Freezing Point Depression: Liquid stays unfrozen at much lower temperatures.
- Boiling Point Elevation: Coolant stays liquid at higher temperatures without boiling.
This combined effect keeps your engine ready for both alpine snow trips and desert summer drives.
Inside the Engine’s Cooling Circuit
Your engine’s cooling circuit is like a looped racetrack for heat transfer. Here’s how coolant circulation works:
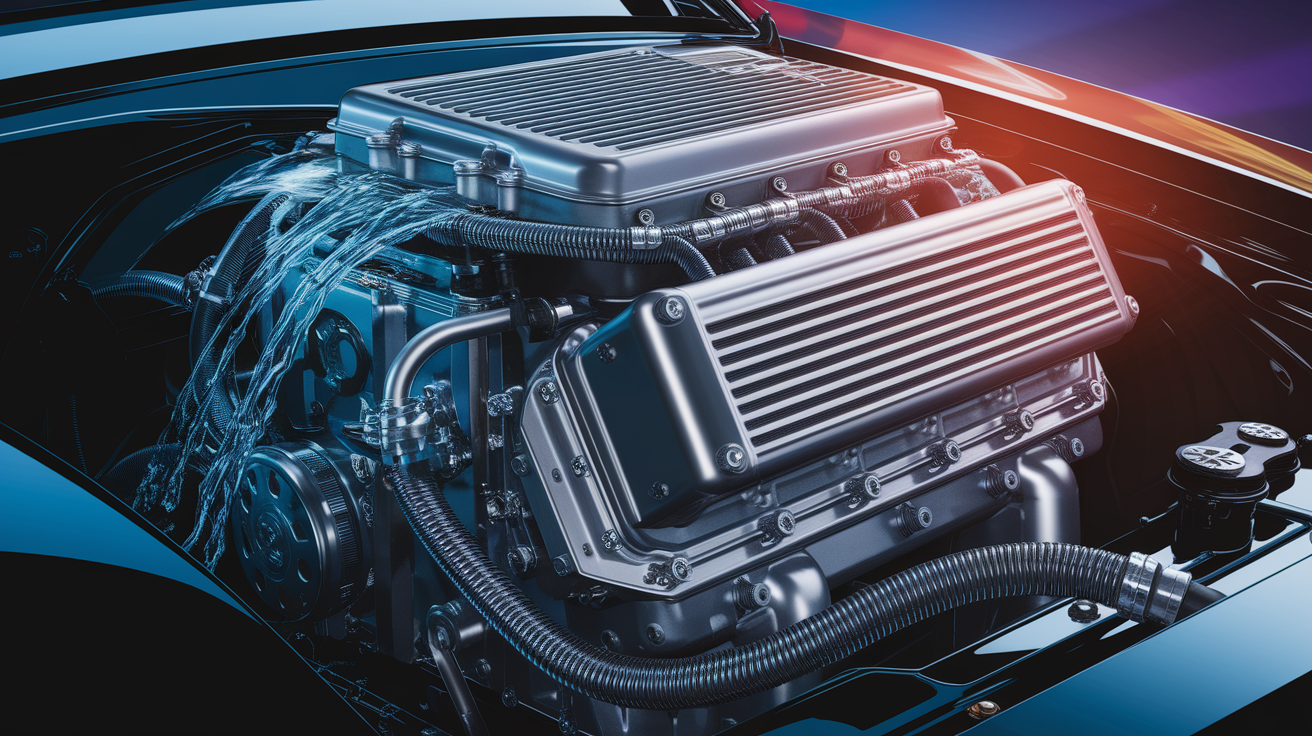

- The water pump pushes coolant through the engine block, absorbing heat from hot metal surfaces.
- The heated coolant travels to the radiator, a heat exchanger that cools the fluid using airflow.
- The thermostat acts like a traffic controller, opening or closing passages to maintain ideal temperature control.
- Once cooled, the fluid loops back into the engine to repeat the process.
In addition to temperature control, antifreeze delivers corrosion inhibitors that stop rust or oxidation from chewing away at metal components inside the cooling system.
What’s in the Mix? Antifreeze Formulations
The two heavy-hitters in antifreeze chemistry are:

- Ethylene glycol: Clear, odorless, excellent at thermal protection but toxic if ingested—commonly used in automotive applications.
- Propylene glycol: Less toxic and used in situations where accidental human or animal contact is possible, like food processing systems or HVAC cooling systems.
Both types disrupt ice formation and boost boiling points, but modern formulas also include additives that fend off corrosion, prevent scaling, and extend the life of cooling system components.
Choosing the right coolant mixture ratio is key—too much water or too much glycol can reduce performance. A 50/50 blend is often ideal for balanced freeze and boil protection.
Handling Hot Topics: Safety and Disposal
Antifreeze safety isn’t just about keeping engines happy—it’s about protecting people, pets, and the environment. Ethylene glycol is toxic and has a sweet taste that can attract animals, making accidental ingestion dangerous. Propylene glycol is safer but not always as thermally efficient.
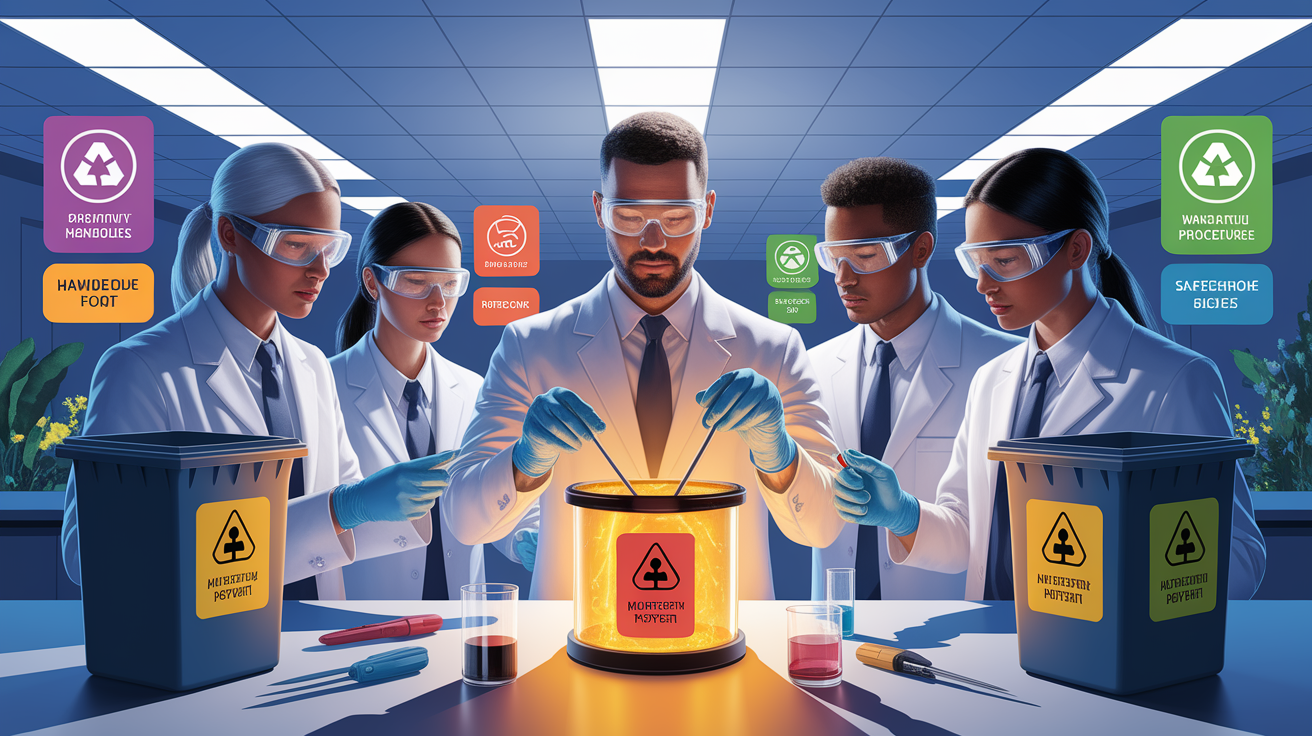

Safe Handling Tips
- Wear gloves and avoid direct skin contact.
- Store away from children and pets.
- Use spill trays during maintenance to catch drips.
Proper Disposal
- Never pour used antifreeze down drains or onto the ground.
- Take it to authorized recycling centers or vehicle service shops.
- Follow manufacturer disposal guidelines for your specific formulation.
Cool as Ice: Summing Up Antifreeze’s Magic
Antifreeze is more than a winter car care essential—it’s a year-round guardian of your vehicle’s thermal health. By altering the coolant’s freezing and boiling points through colligative properties, it ensures smooth engine temperature regulation in all climates. Add in its role in engine protection against corrosion, and you’ve got one of the unsung heroes of vehicle maintenance. Whether you drive in icy mountains or scorching deserts, a properly managed antifreeze mixture keeps your engine cool under pressure—and warm when it matters most.













